Beijing Then and Now
Beijing Then
Beijing, the capital of the People’s Republic of China, has played a pivotal role in the nation’s political and cultural history for over eight centuries.
Known as the “Northern Capital,” the name Beijing was officially adopted in 1403 during the Ming dynasty to differentiate it from Nanjing, or “Southern Capital.”
The city has been known by various names throughout its 3,000-year history, with “Peking” being a notable earlier English spelling, which dates back to the 17th century.
This spelling was popularized by Jesuit missionary Martino Martini in a 1655 atlas.
While “Peking” is largely obsolete today, remnants of this nomenclature persist in names of places such as Peking University and the IATA code PEK for Beijing Capital International Airport.
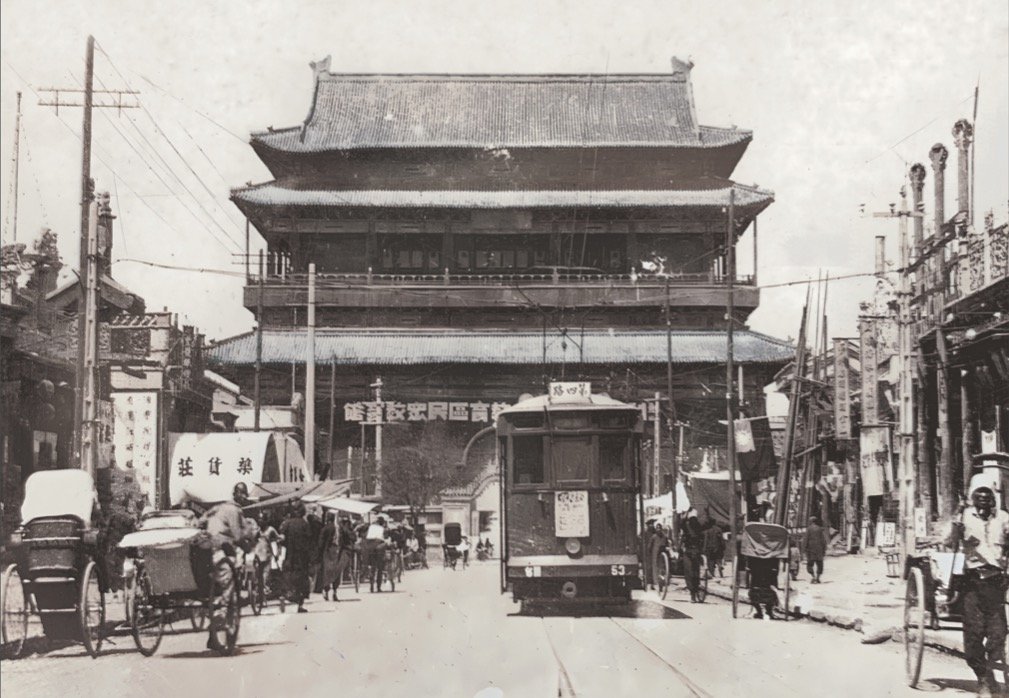

The abbreviation for Beijing in Chinese, 京, is also used on local automobile license plates, while the official Latin alphabet abbreviation is “BJ.”
Understanding Beijing is essential for comprehending the broader historical and cultural narratives of China.
Related Article: Mumbai Then and Now
Beijing History
Beijing, the capital of China for nearly eight centuries, boasts a rich and complex history that dates back to prehistoric times.
Fossil remains of Peking Man, dating from 770,000 to 230,000 years ago, were discovered at Zhoukoudian, highlighting early human habitation in the region.
Approximately 3,000 years ago, Neolithic communities settled near the site of modern Beijing.
The city’s history as a political center began during the Warring States period (475–256 BC) when the kingdom of Yan established its capital, Ji, at the present site of Beijing.
Related Article: Kuala Lumpur Then and Now
Throughout its early history, the city saw several transitions. Following the Qin dynasty’s unification of China, the capital city was destroyed but later rebuilt during the Han dynasty, maintaining its significance as a provincial town amid conflicts with nomadic tribes.
Over the centuries, the area was controlled by various powers, including the Khitans, who founded the Liao kingdom, and later the Juchen, who established the Jin dynasty, renaming the city Zhongdu.
In the early 13th century, Genghis Khan’s Mongol forces conquered the Jin, leading to the establishment of the Yuan dynasty under Kublai Khan, who named the new capital Dadu (“Great Capital”).
This marked Beijing’s emergence as the political center of China. The city was significantly enlarged, featuring impressive architecture influenced by both Mongolian and Chinese styles.
Related Article: Bangkok Then and Now
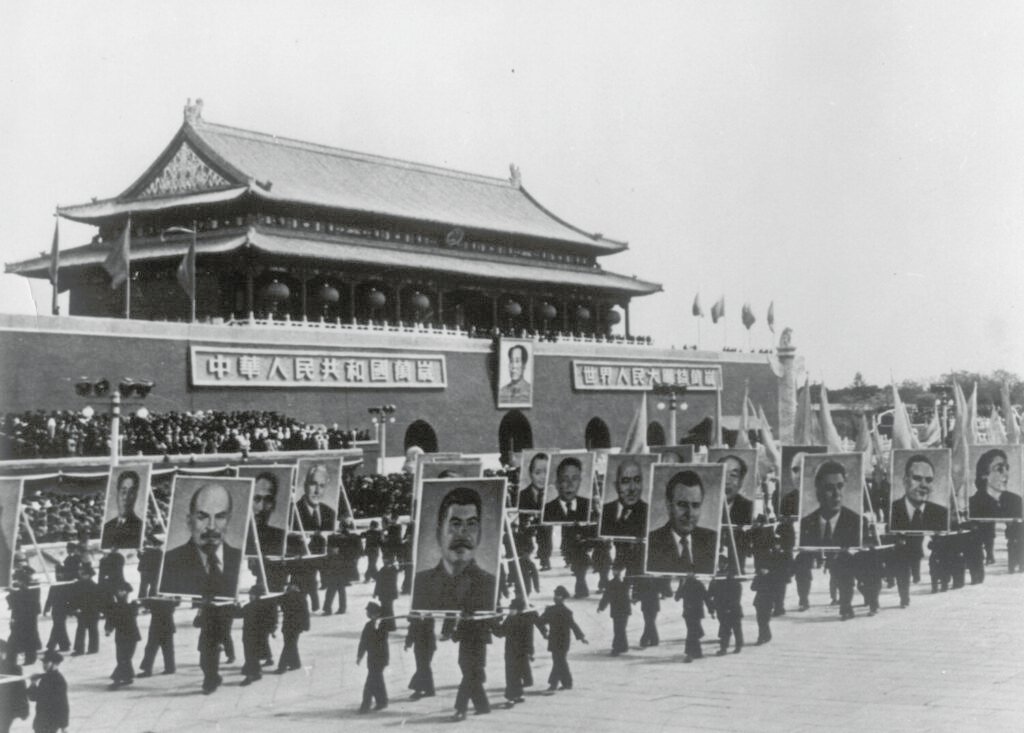

The Ming dynasty (1368–1644) solidified Beijing’s status, with the city being renamed again to Beijing (“Northern Capital”) under the Yongle Emperor in 1403.
The city underwent further development, with new walls and structures built, primarily in the 15th century, reflecting the grandeur of the Ming era.
The Qing dynasty (1644–1912) maintained the city’s layout while expanding its cultural and architectural significance with palaces and temples.
Despite external pressures, including the Boxer Rebellion and foreign occupation, Beijing remained a vital political hub.
After the fall of the Qing dynasty, Beijing briefly lost its status as the capital during the Republican era, only to regain it in 1949 with the establishment of the People’s Republic of China.
Related Article: Seoul Then and Now
Since then, Beijing has transformed significantly, evolving into a modern metropolis while still preserving its historical heritage.
Urban development accelerated in the late 20th century, particularly post-1980s, leading to the construction of new infrastructure and a burgeoning middle class.
The city underwent a dramatic transformation in preparation for the 2008 Summer Olympics, with extensive improvements in transportation and urban facilities.
Today, Beijing stands as a dynamic center of culture, politics, and economic growth, grappling with modern challenges such as air pollution and urban congestion, while also celebrating its rich historical legacy.
Related Article: Tokyo Then and Now
Beijing Now
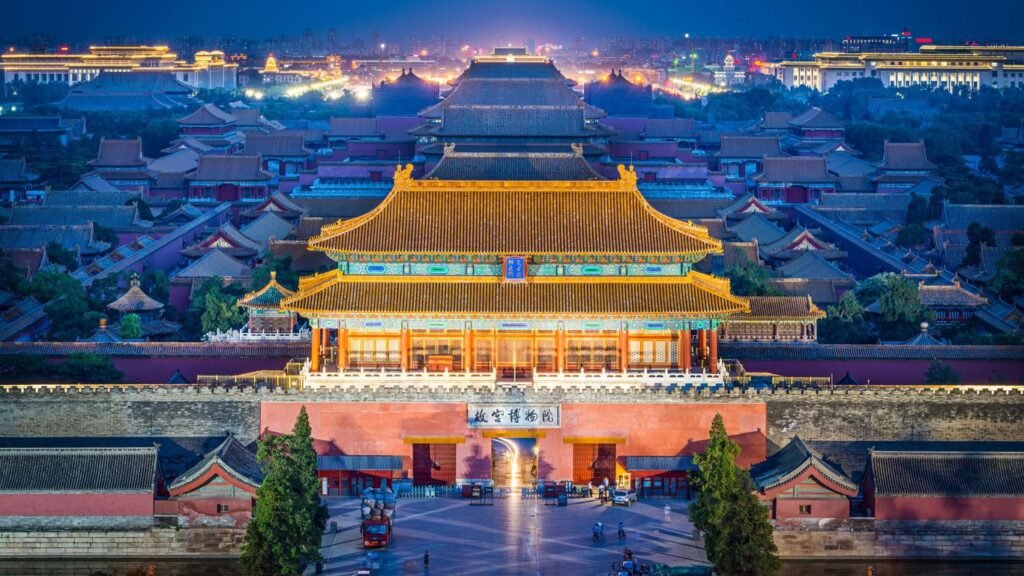

Beijing, the capital city of China, stands as a vibrant metropolis with a rich historical heritage and a modern dynamic.
With over 22 million residents, it is not only the world’s most populous national capital but also the second-largest city in China, following Shanghai.
Strategically located in Northern China, Beijing functions as a municipality directly governed by the State Council, encompassing 16 districts that range from urban to rural areas.
Its geographical positioning is significant, bordered by Hebei Province and in proximity to Tianjin, collectively forming the Jing-Jin-Ji cluster, a key economic region.
Related Article: Hong Kong Then and Now
As a global city, Beijing plays a pivotal role in various domains such as culture, diplomacy, finance, and technology.
It hosts the headquarters of many of China’s largest state-owned enterprises and boasts the highest number of Fortune Global 500 companies in the world.
This financial prowess is complemented by the presence of the world’s four largest financial institutions by total assets.
The city’s transportation infrastructure is highly developed, serving as a major hub for national highways, expressways, railways, and high-speed rail networks.
Related Article: Dubai Then and Now
The Beijing Capital International Airport, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, was Asia’s busiest airport, indicating the city’s significance in global connectivity.
Additionally, the Beijing Daxing International Airport, which opened in September 2019, is notable for being the largest single-structure airport terminal globally, further enhancing the city’s transportation capacity.
Beijing’s influence extends into the realm of international sporting events, having hosted the 2008 Summer Olympics and Paralympics, which left a lasting legacy in terms of infrastructure and global recognition.
Related Article: Singapore Then and Now
In a historic feat, Beijing became the first city to host both the Summer and Winter Olympics, along with their respective Paralympics, in 2022.
This achievement underscores Beijing’s role as a leading global city, adept at managing large-scale international events.
Despite the closure of Beijing Nanyuan Airport for civilian use following the opening of Daxing Airport, the city maintains a network of airports that continue to facilitate air travel, albeit primarily for military purposes.
Overall, Beijing exemplifies a blend of ancient tradition and cutting-edge modernity, making it a key player on the world stage.
Related Article: Shanghai Then and Now
FAQs
Beijing is famous for its rich history, cultural heritage, and significant political role as the capital of China.
It is home to iconic landmarks such as the Great Wall, the Forbidden City, and Tiananmen Square.
Additionally, Beijing is a center for arts, education, and international diplomacy, hosting numerous global events and conferences.
Beijing is located in mainland China. It is the capital city of the country, while Hong Kong is a Special Administrative Region (SAR) of China situated on the southern coast.
The main city in China is Beijing, serving as the political and cultural capital.
However, Shanghai is the largest city in terms of population and is a major financial hub.
The main sources of income in Beijing include finance, technology, tourism, and trade.
The city is a hub for state-owned enterprises, multinational corporations, and a growing tech industry, contributing significantly to its economy.
Tourism also plays a vital role due to the city’s historical and cultural attractions.