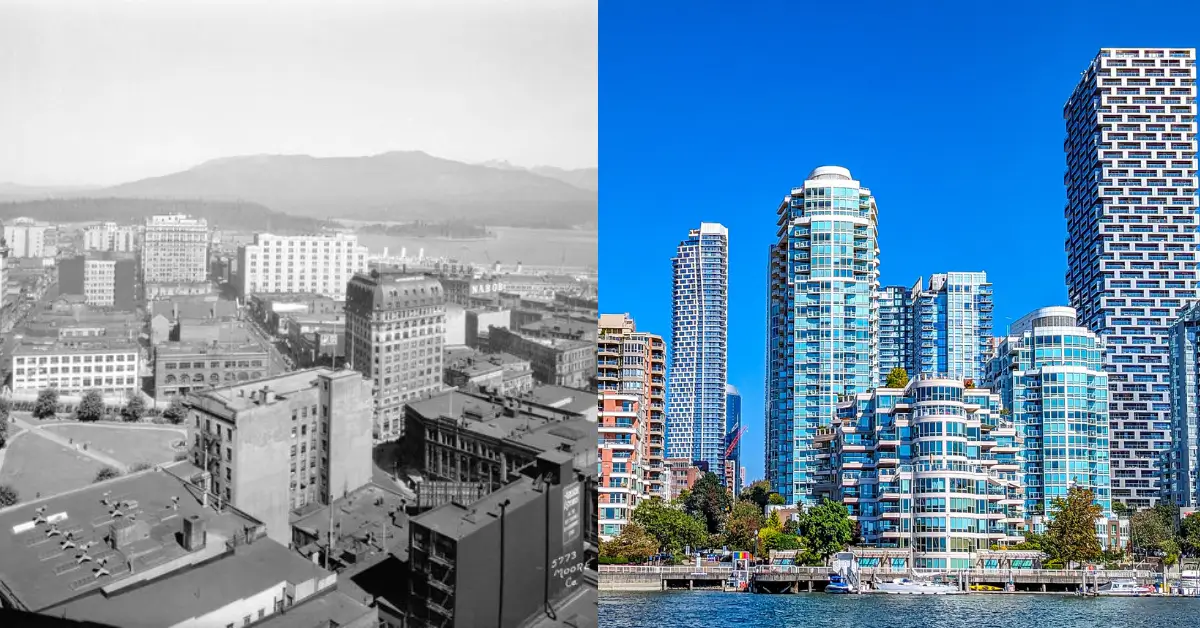
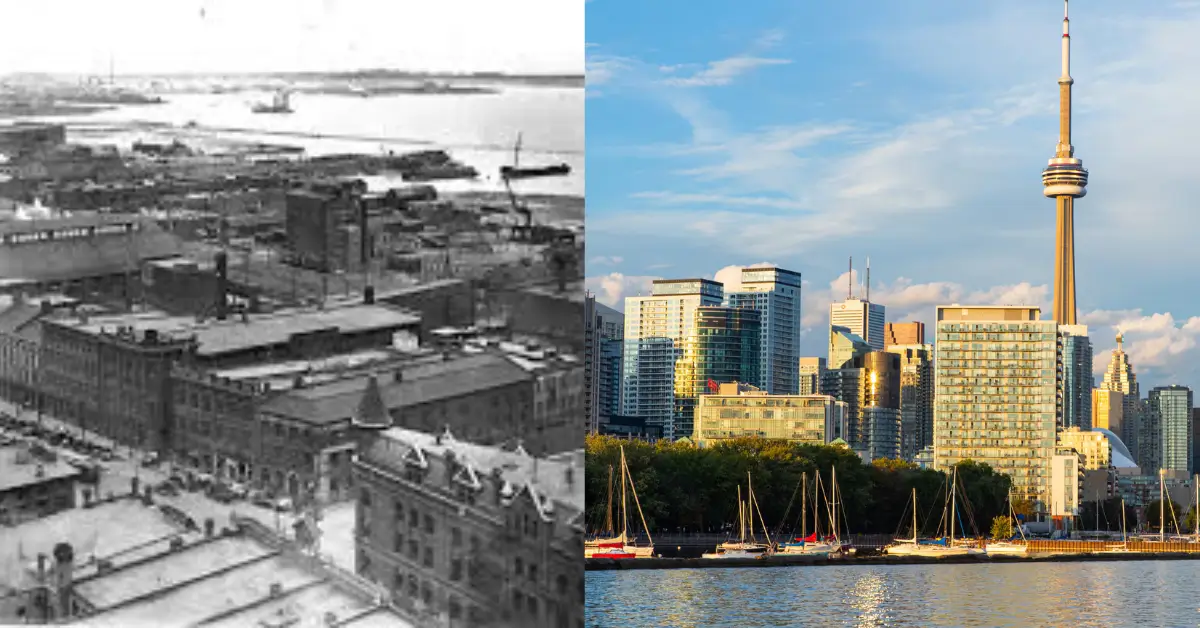
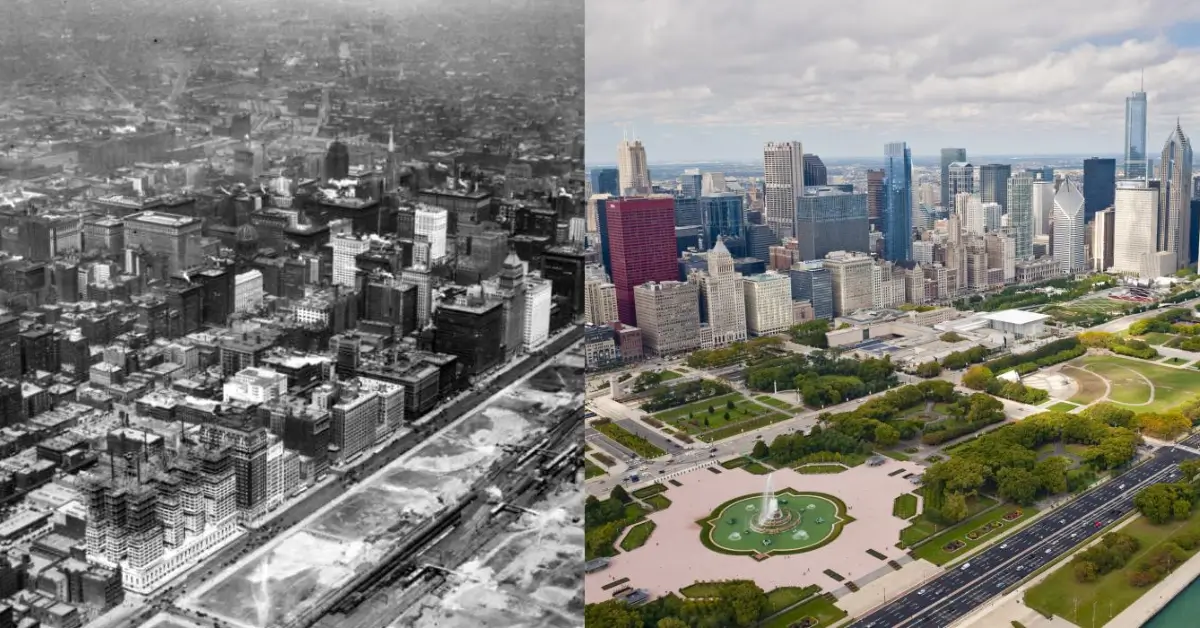
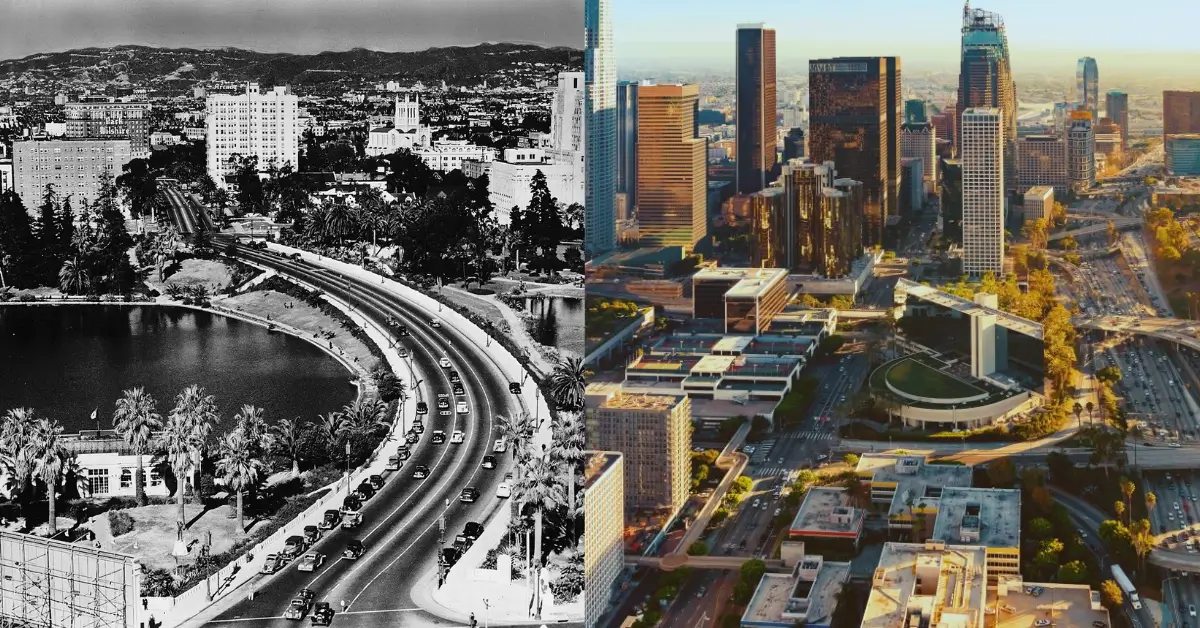
Dubai Then and Now
Dubai Then
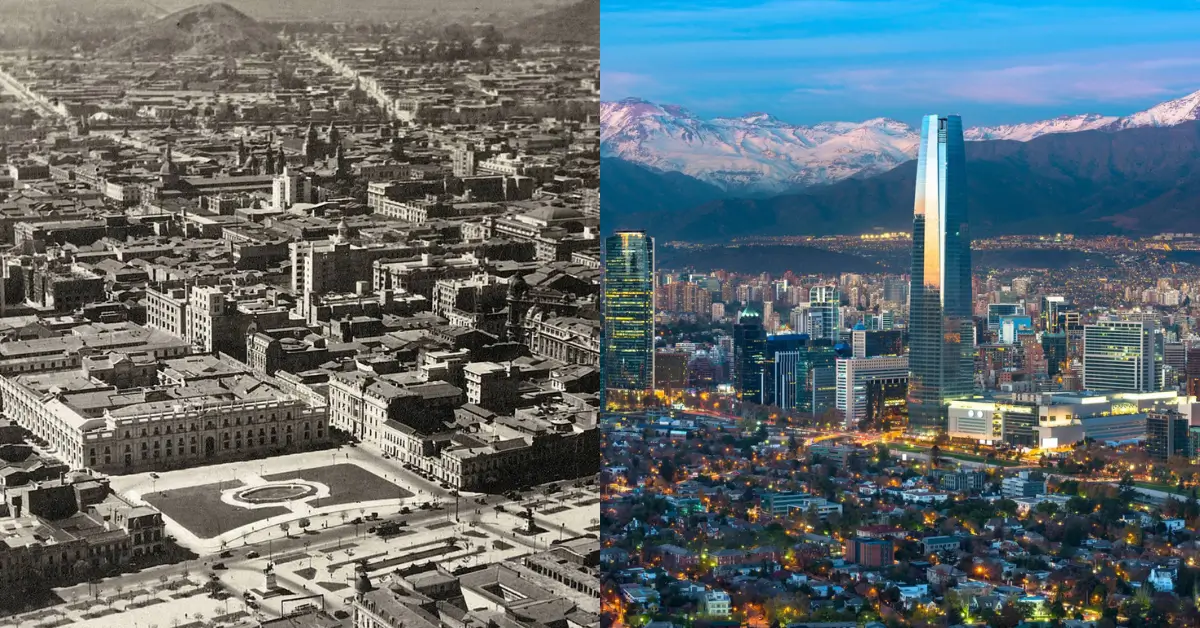
Dubai, the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, is one of the seven emirates that make up the United Arab Emirates (UAE), a federation established in 1971 after gaining independence from British rule.
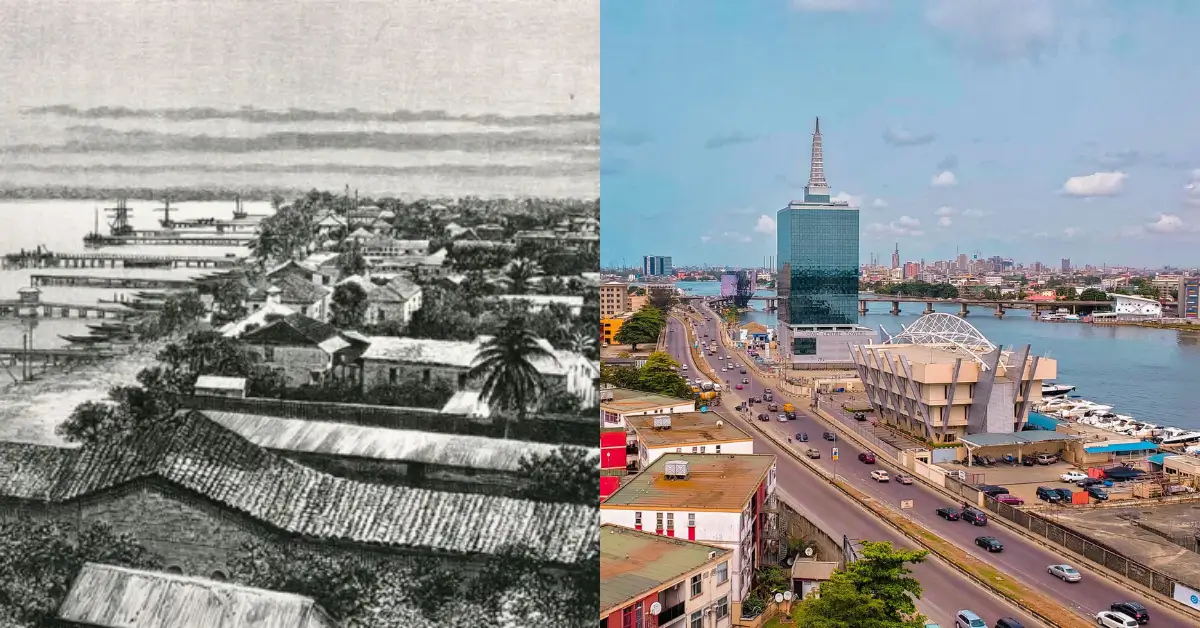
Known for its remarkable wealth and rapid development, Dubai has transformed from a modest fishing village into a global metropolis renowned for its skyscrapers, luxury shopping, and vibrant tourism industry.
The origins of the name “Dubai” are subject to various theories; one suggests it derives from “daba,” referring to a type of locust that was once common in the area, while another posits that it comes from a historical market that existed near the city.
Regardless of its etymology, Dubai has emerged as a symbol of modernity and innovation in the Middle East, attracting millions of visitors and businesses from around the world.

Dubai History
The history of human settlement in the area now known as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a rich tapestry woven through thousands of years, reflecting complex interactions among various civilizations and the evolution of trade.
The archaeological record indicates that the region was inhabited as early as the Ubaid and Hafit periods, with notable finds in Dubai, particularly in areas like Al-Ashoosh and Saruq Al Hadid.
During these early times, the region was known as Magan to the Sumerians and was recognized for its metalwork, especially copper and bronze.
Related Article: Singapore Then and Now
As the coastline shifted approximately 5,000 years ago, the area became less hospitable to settlement, leading to a reliance on trade with distant lands, including the Indus Valley and Mesopotamia.
Pre-Islamic artifacts from the 3rd and 4th centuries reveal a continued human presence, with the local population practicing a form of polytheism before the advent of Islam.
The spread of Islam in the 7th century significantly influenced the region’s cultural landscape.
The Umayyad Caliphate expanded into southeast Arabia, with archaeological finds from this period in Jumeirah indicating the area’s growing importance.
Early mentions of Dubai date back to 1095, and by the late 16th century, the Venetian pearl merchant Gasparo Balbi noted Dubai’s thriving pearling industry.
Related Article: Shanghai Then and Now
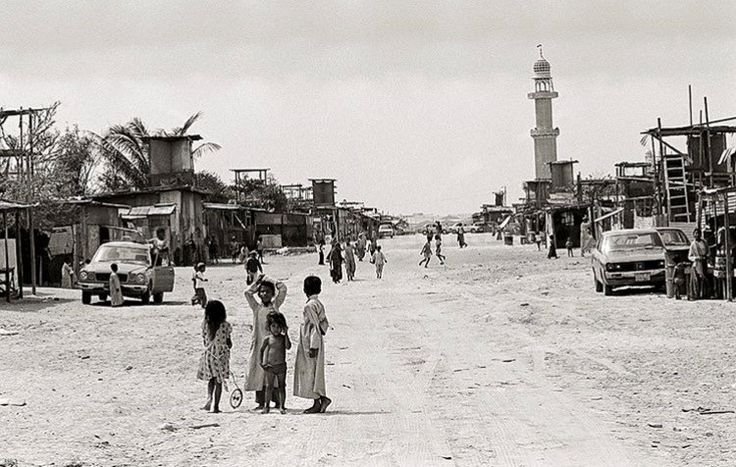
In the early 18th century, Dubai emerged as a small fishing village. By 1822, it had developed into a town with around 800 residents belonging to the Bani Yas tribe, under the rule of Sheikh Tahnun bin Shakhbut of Abu Dhabi.
A significant turning point came in 1833 when members of the Al Bu Falasah tribe, led by Maktoum bin Butti, seceded from Abu Dhabi and established the Maktoum dynasty in Dubai.
The British established a presence in the region, leading to treaties that facilitated security and stability, which further encouraged trade.

A smallpox epidemic in 1841 and subsequent fires tested the resilience of the community, but by the end of the 19th century, Dubai had established itself as a free port, attracting merchants from the surrounding region and beyond.
The pearling industry thrived until the late 1920s, when the Great Depression and the advent of cultured pearls devastated the local economy, resulting in widespread poverty.
Related Article: Hong Kong Then and Now
However, a pivotal moment in Dubai’s history came in 1937 with the signing of an oil exploration contract.
While oil was not discovered until 1966, this anticipation set the stage for dramatic growth.
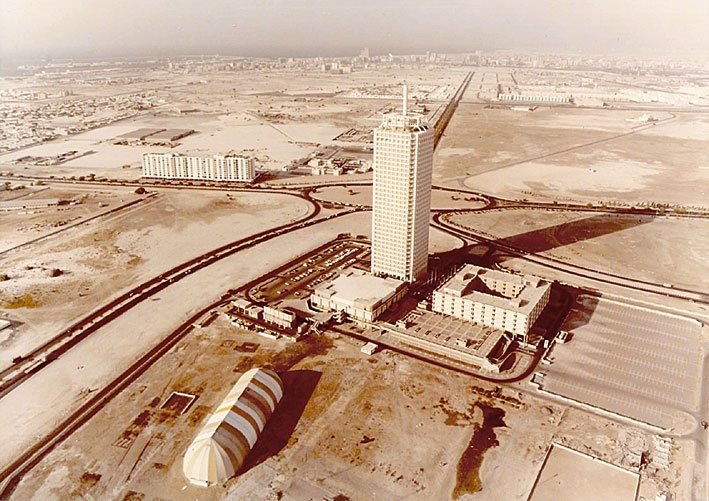
Post-World War II, under Sheikh Rashid bin Saeed Al Maktoum, Dubai began significant infrastructure development using trade revenues.
The establishment of an airport in 1960 and subsequent infrastructure projects laid the groundwork for modern Dubai.
The discovery of oil in 1966 transformed Dubai’s economy, prompting rapid population growth and further development.
Related Article: Tokyo Then and Now
As the emirate evolved, it diversified its economy beyond oil, focusing on trade, tourism, and real estate, which has led to the vibrant, global city we see today.
Dubai’s transformation from a modest fishing village to a major international hub is a testament to its strategic location, visionary leadership, and resilient community.
Dubai Then

Dubai is the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and serves as the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, which is the most populated among the country’s seven emirates.
With a population of approximately 3.79 million as of 2024, Dubai stands out for its diverse demographic, with over 90% of its residents being expatriates.
This significant expatriate community reflects the city’s welcoming environment and its global appeal, attracting individuals from various cultures and backgrounds.
Related Article: Seoul Then and Now
Originally founded in the 19th century as a humble fishing village, Dubai has undergone a remarkable transformation over the decades.
Starting in the early 20th century, it evolved into a crucial regional and international trade hub, focusing heavily on tourism and luxury services.
This evolution has been fueled by the city’s strategic location on the eastern Arabian Peninsula, bordering the Persian Gulf, which has made it an ideal gateway for trade and commerce.
Oil revenue played a pivotal role in accelerating the city’s development; however, by 2018, oil production accounted for less than 1% of Dubai’s GDP, signaling a shift toward a more diversified economy.
Today, Dubai is renowned for its extravagant lifestyle and luxury amenities.
Related Article: Bangkok Then and Now
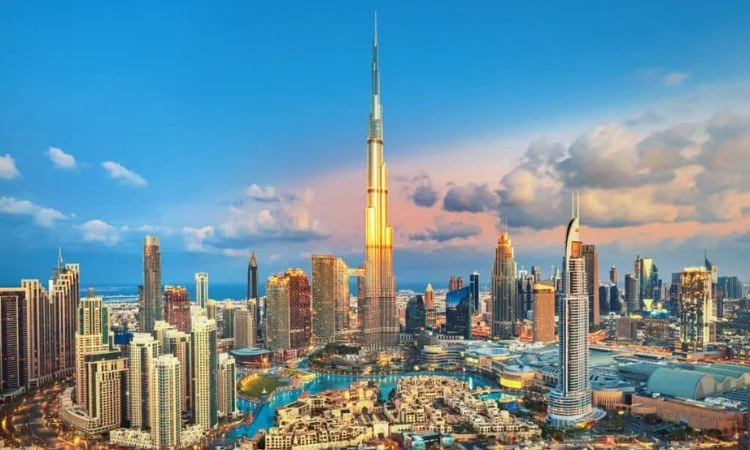
It boasts the second-highest number of five-star hotels in the world and is home to the Burj Khalifa, the tallest building globally, standing at an impressive 828 meters (2,717 feet).
This architectural marvel is not only a symbol of the city’s rapid growth and ambition but also a major tourist attraction.
In 2023, Dubai was recognized as the third most-visited city in the world, reflecting its status as a premier destination for travelers seeking both leisure and business opportunities.
The city’s economy now relies on a variety of sectors, including trade, tourism, aviation, real estate, and financial services, which together create a vibrant and dynamic urban landscape.
Related Article: Kuala Lumpur Then and Now
FAQs
Dubai is a city and also the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, one of the seven emirates that make up the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Dubai was founded in the 19th century as a small fishing village. Its strategic location along trade routes led to its growth as a center for commerce, with significant development occurring in the early 20th century.
The name “Dubai” is believed to be derived from the Arabic word “daba,” which means “to creep” or “to move slowly,” possibly referencing the movement of the Dubai Creek or the local wildlife.
Some sources suggest it may also relate to the season in which locusts appear, called “yadub,” as locusts were a significant part of the area’s history.
The state name of Dubai is the Emirate of Dubai. It is one of the seven emirates that comprise the UAE, each governed by its own monarch.